
Heatmaps very clearly and intuitively with color gradients, highlight areas of high/low activity & make it easy to identify patterns at a glance.
It helps identify areas of concentration, often referred to as "hotspots." This information can optimize design, or identify areas of demand.
It can be used to track changes in data over time, allowing you to identify emerging trends, patterns, and evolving customer behavior.
It can be used to compare different datasets, allowing you to identify similarities, differences, best practices, & different interventions.
A step-by-step guide for creating a Heatmap through QuickGraphAI Editor:
Ensure your data is organized in a table format, with rows and columns representing the variables you want to visualize.
You can usually copy and paste your data from a spreadsheet or manually input it. Make sure your data is correctly formatted for the tool to interpret.
You can customize the color scheme, scale, and labels of your heatmap. We also allow you to adjust the intensity and range of the colors.
Once your data is entered and settings are adjusted, generate your heatmap. The tool will create a visual representation of your data, showing the intensity of values through color gradients.
Once you generate the heatmap, you can download it in different formats, such as PNG, JPEG, SVG, and PDF, or share it directly from the tool.
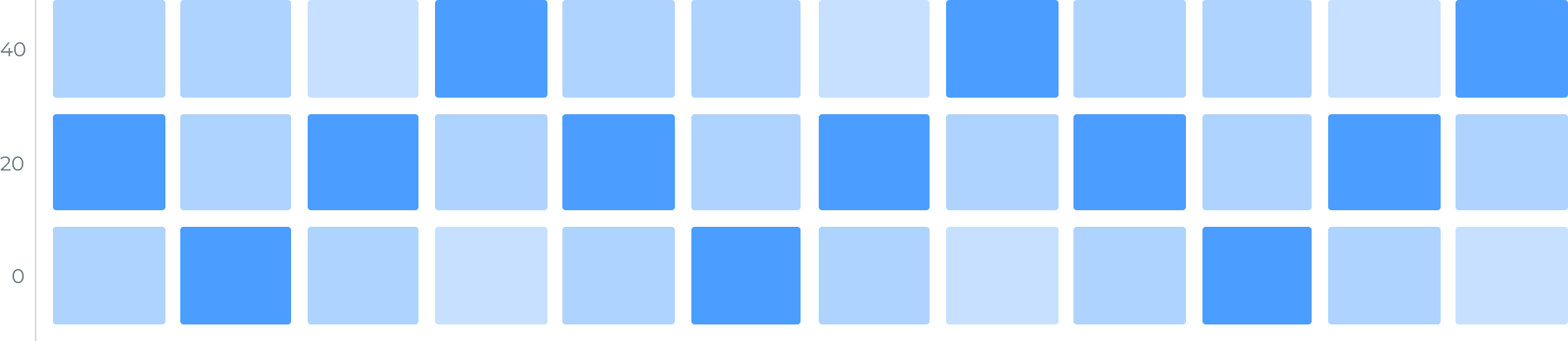

Heat maps have been extremely useful because they allow you to both simplify and visualize data analysis. Examples of when to use a heat map include business analysis, website user behavioral analysis (such as where website visitors are clicking or hovering with the mouse), exploratory data analysis, geographic visualization, and many more examples.
There are two major types of heat maps: cluster heat maps and diverging heat maps.
A spatial heat map depicts the intensity of a spatial phenomenon as color, typically projected over a map. They can be used, for instance, to show temperature differences around the world by a color gradient ranging from blue to red for hot and cold, respectively.
A grid heat map represents values for two variables of a category across a two-dimensional matrix of colored squares. The color scale (with the intensity of the hue) of the grid is used to highlight significant values. Grid heat maps can be further split into two different types: correlograms and clustered heat maps.

QuickGraph AI Editor transformed how we present data. The AI-powered insights and seamless interactive editor make complex visualizations effortless and dynamic. It was like having a data scientist and a designer in one tool!
Explore our insightful blog posts

All Rights Reserved. © 2026 by QuickGraph.